Everything you need to know about diodes
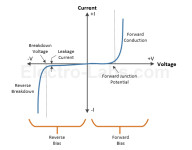
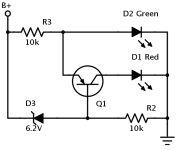
Diodes are commonly used discrete semiconductor devices. It has many uses and purposes. Its operation is based on PN semiconductor junction characteristics. Depending on diode’s physical and chemical properties, it can behave very differently. Together with other electronic components diode can be used for voltage clipping, multiplying, rectifying, signal, demodulation, protection, and even more. Elektro-labs have written a pretty nice review of diode types and their common uses. The simplest and probably most recognizable is regular diode which is used in switching, protection rectification circuits. Another common diode type is Zener which is used for voltage stabilization. Here are some of the most common types of diodes, along with examples of part numbers: