Few tips for building reliable SPI interface
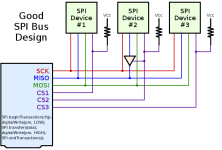
Many SPI tutorials use the standard notation of bus design where each device is directly in parallel connected to SCK, MISO, MOSI, and CS lines. This usually works without a problem, but there can be problems when more than one SPI device is on the bus. There might be several issues that can occur on poor design. Here are three suggestions for better SPI improvements: Pull up resistor helps to prevent the response from multiple devices at once. This might come from poor software design when CS pins aren’t appropriately initialized. The second problem is with MISO pin. Some SPI devices don’t enter tri-state even when CS is pulled high. So when talking to other SPI devices this will cause failures. Be sure to check if SPI device supports tri-state when inactive; otherwise, add external tri-state buffer like 74AHC1G125. And last thing is SPI transactions. In systems where multiple SPI devices are used, there is a risk of using different settings that were selected on different devices. Most importantly, transactions can ensure exclusive use of the SPI bus when needed….